Ground-Mounted Solar Mounting Solution
Solution Overview
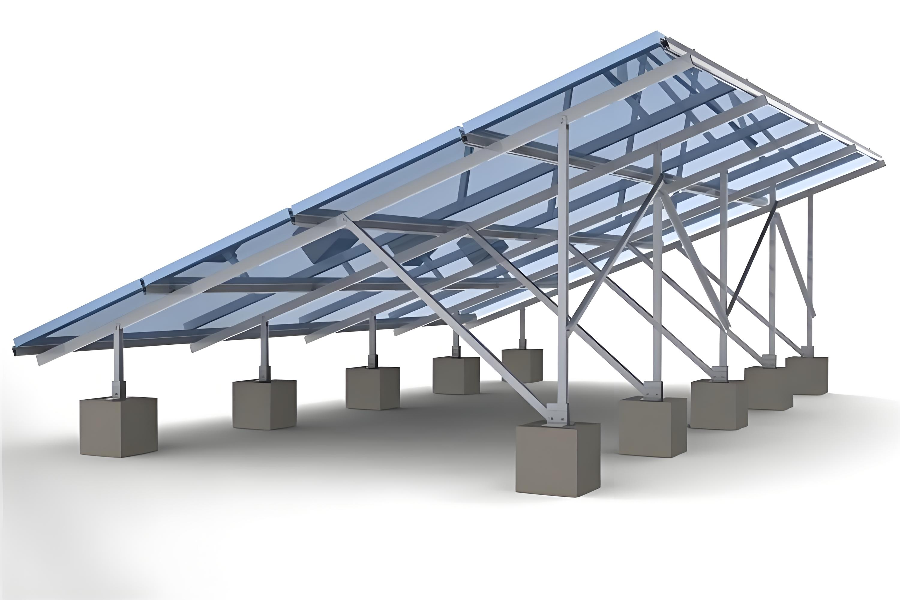
Ground-mounted solar mounting systems are critical structural systems designed to support photovoltaic modules and ensure long-term stability.
They are primarily composed of vertical posts, horizontal beams, and diagonal braces, working together to bear module weight as well as environmental loads such as wind and snow.
The system design must comprehensively consider geological conditions, climate factors, and cost efficiency to ensure safe operation and a service life exceeding 25 years.
Structural Components & Functions
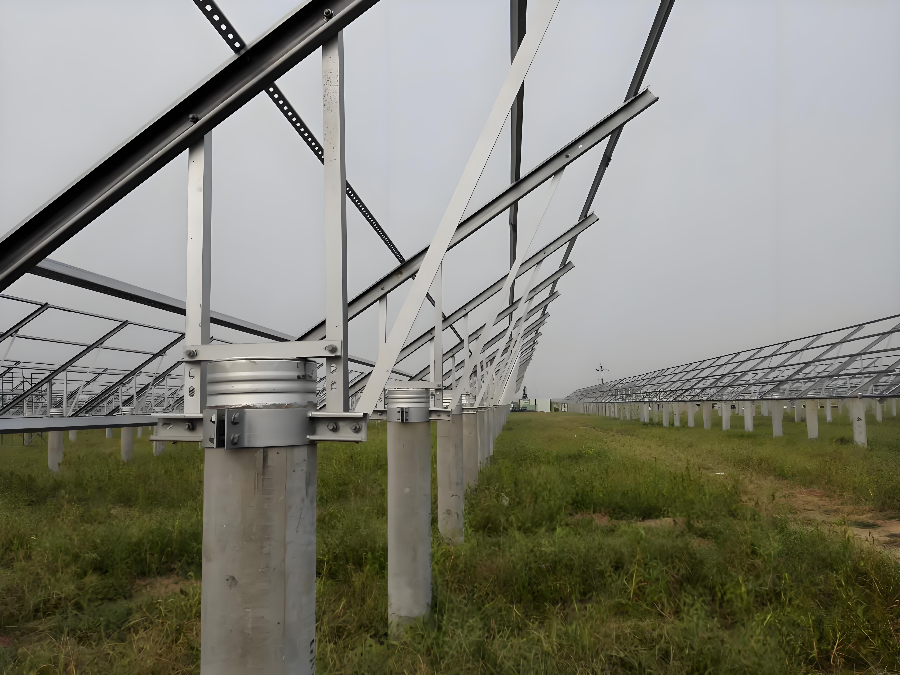
Vertical Posts
Vertical posts serve as the primary foundation elements and are directly anchored to the ground.
They are typically manufactured from hot-dip galvanized steel or aluminum alloy.
Galvanized steel offers high strength and excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for complex environments.
Aluminum alloy provides lightweight construction and convenient installation.
Post embedment depth and spacing are calculated based on soil bearing capacity.
In soft soil conditions, deeper embedment and reduced spacing are applied to enhance overall stability.
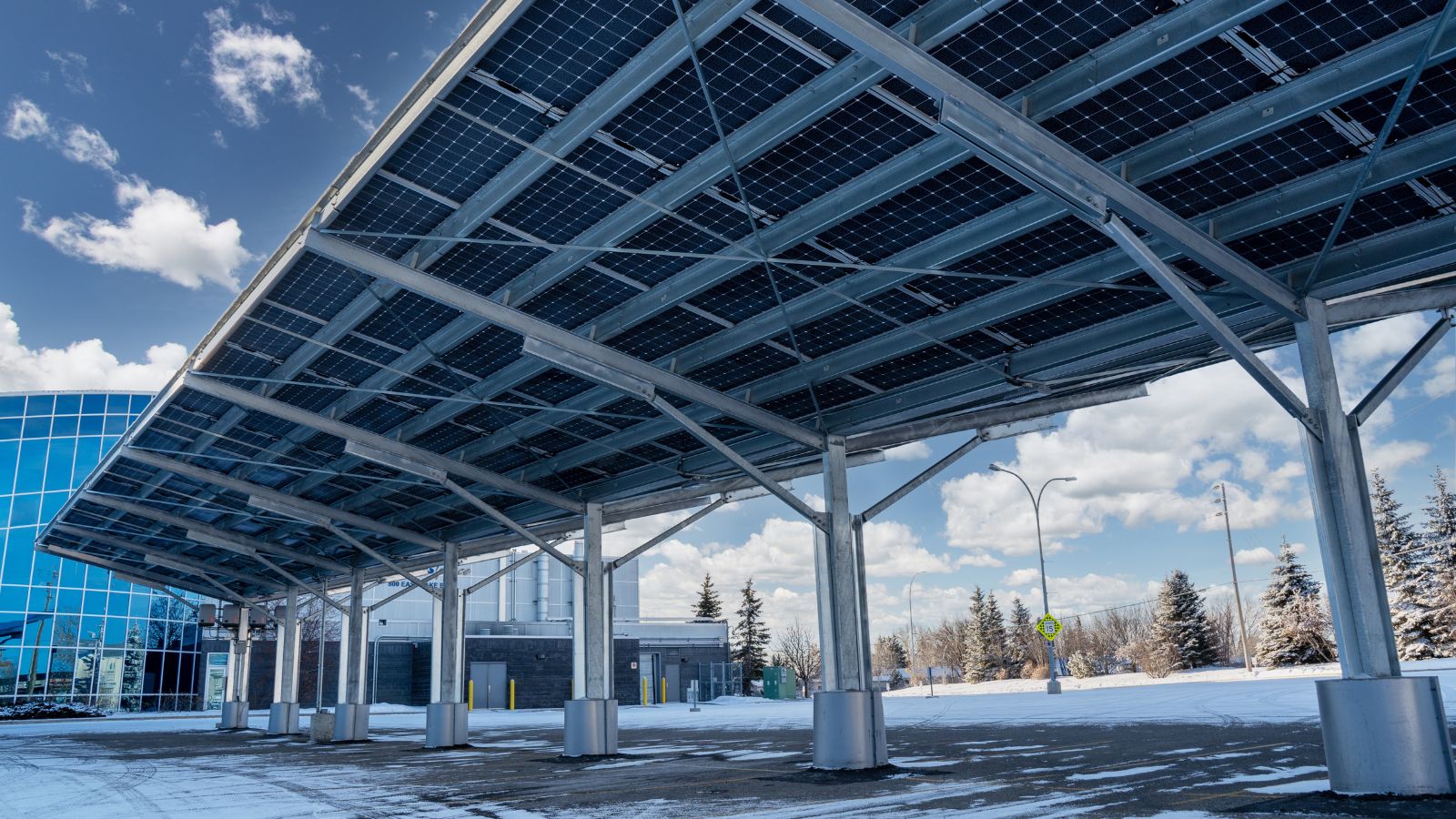
Horizontal Beams & Diagonal Braces
Horizontal beams support vertical loads from PV modules, while diagonal braces improve resistance to wind and snow loads.
Additional components such as vertical supports, braces, and clamps are connected by bolts to form a rigid structural system, effectively preventing structural deformation.
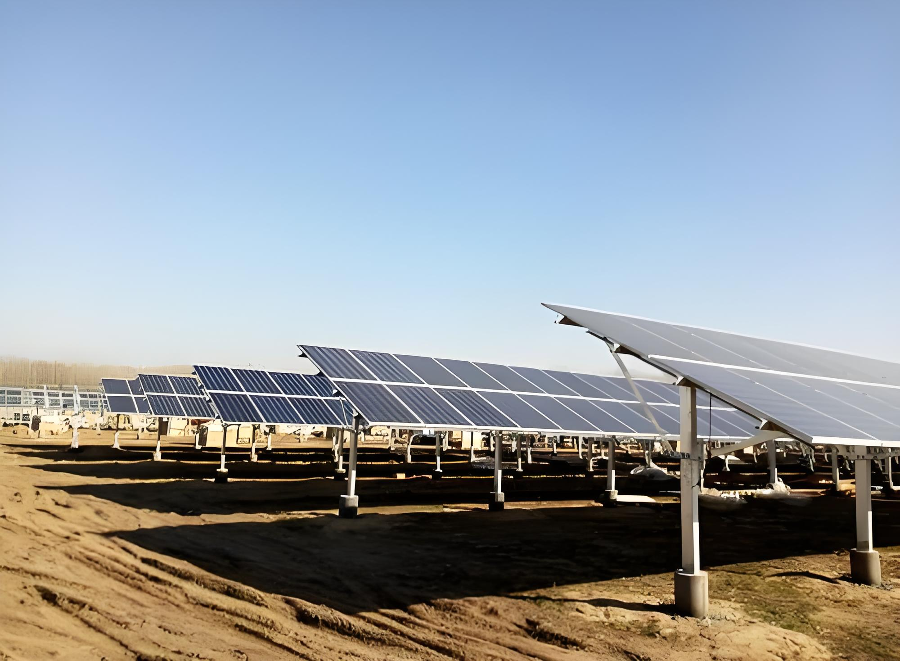

Common System Types & Characteristics
Ground-mounted solar structures are generally classified into:
Fixed-Tilt Mounting Systems
Simple structure, low cost, and minimal maintenance requirements.
Widely used on flat terrain with stable ground conditions.Adjustable-Tilt Mounting Systems
Allow manual adjustment of module tilt angle, increasing energy yield by approximately 5%.
However, adjustment mechanisms may increase mechanical complexity.Solar Tracking Mounting Systems
Systems such as single-axis trackers dynamically follow the sun’s trajectory, increasing power generation by 15%–30%.
These systems require higher initial investment and maintenance.
For complex terrain, pile-driven mounting systems combining hot-dip galvanized steel piles with aluminum rails provide flexible adjustment and high installation efficiency, making them suitable for mountainous or sloped sites.
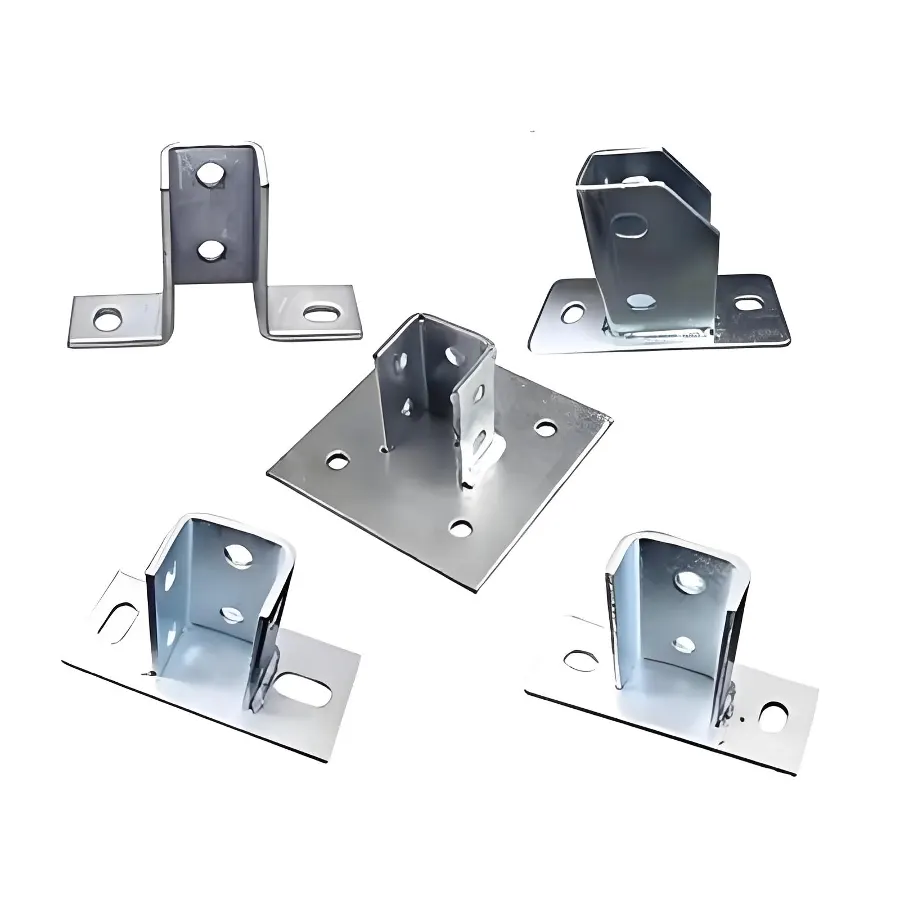

Hot-Dip Galvanized Base Support
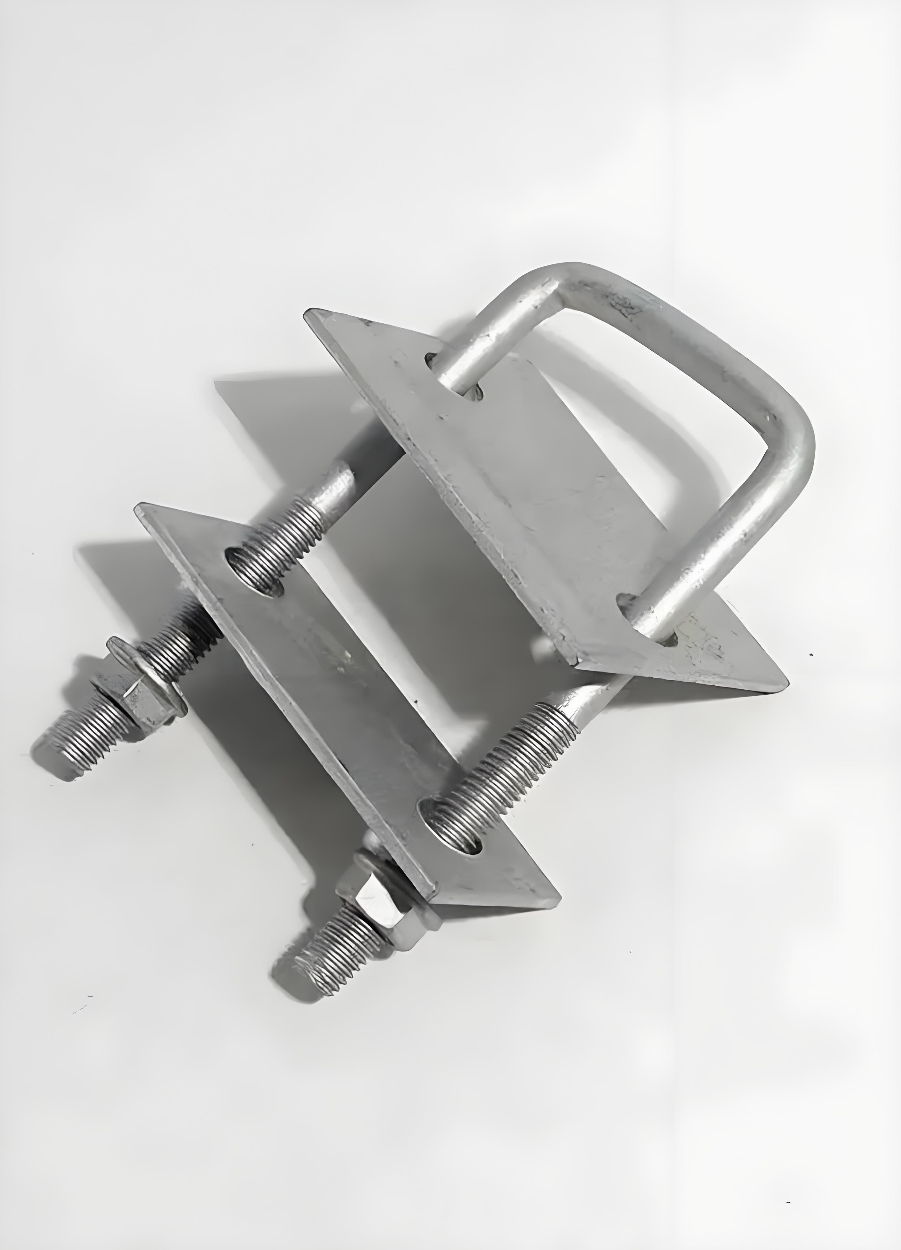

Hot-Dip Galvanized Square Tube Module Clamp
Material Selection & Corrosion Protection
Material selection directly affects durability and service life. Common materials include:
Hot-dip galvanized steel
Aluminum alloy
Zinc-aluminum-magnesium coated steel
Hot-dip galvanizing forms a protective zinc layer on steel surfaces to prevent corrosion.
Closed sections are designed with drainage holes to avoid internal pressure during galvanizing.
Zinc-aluminum-magnesium steel profiles are cold-formed and not welded, offering superior corrosion resistance.
Aluminum components are treated with anodizing for enhanced surface protection.
Additional corrosion protection measures include:
Avoiding welding damage to protective coatings
Using stainless steel fasteners (SUS304 / SUS316)
Selecting enhanced corrosion-resistant materials in highly corrosive environments
Installation Methods & Environmental Adaptability
Common installation methods include:
Pile driving
Embedded anchor bolts
Concrete foundations
Pile-driven systems allow rapid installation with piles driven 1–2 meters into the ground, significantly reducing construction time.
Typical system parameters include:
Tilt angle: 5°–45°
Span: 1.2–2.0 meters
Installation tolerance: ±2°
In regions with wind speeds exceeding 60 m/s or snow loads above 1.4 kN/m², reinforced post stiffness and enhanced foundation anchoring are applied.
Flexible mounting systems are also available for irregular terrain, adapting to uneven ground and improving land utilization efficiency.



